Wind Plant Transient Evaluation Studies
Power system apparatus, such as transformers, switchgear, and cables may be exposed to various types of transients. High-frequency transients and very steep overvoltages may cause problems for electrical equipment because they can cause local overstressing of the insulation system. Wind plant collector circuit breaker opening-and-closing operations and lightning surge events are important potential sources of these high rate-of-rise transients.
A transient analysis was performed for a wind plant design which utilizes larger amounts of generation on feeder circuit breakers. The studied wind farm power system included a circuit with 39 – GE 2.72 MW wind turbines and a very long feeder circuit with a home-run cable section of 21,995 feet and a total collector circuit of 213,985 feet. The transient studies had several objectives, including an evaluation of temporary overvoltage (TOV) conditions to review grounding transformer and MOV surge arrester ratings, an evaluation of BIL ratings of the turbine transformers confirming 150 kV BIL levels are sufficient for equipment on the plant collection feeders, an evaluation of feeder circuit breaker switching transients including restrikes, pre-strikes, and current chopping events, and an evaluation of different neutral grounding reactors (NGR) ratings during substation lightning surge events.
High-frequency transient simulation models of the required next generation wind plant substation, collector circuits, and the adjacent power system equipment were created. The transient simulation models consisted of the required equivalent sources and transfer impedances, π-section and traveling wave transmission line and underground cable models, substation transformers, shunt capacitor banks, MOV surge arresters, and the appropriate circuit breaker and substation load characteristics. The analysis for the different transient studies was completed using the EMTP-RV simulation program.
The results for these studies included a summary of transient simulations and equipment BIL rating analysis completed during an insulation coordination evaluation of the next generation wind plant substation. Insulation coordination is defined in IEEE Std. 1313.2 as the selection of insulation strength consistent with expected overvoltages to obtain an acceptable risk of failure. The degree of coordination is measured by the protective ratio, which is defined as the insulation withstand level divided the voltage at the protected equipment. A review of the protective ratios and insulation coordination for the equipment in the next generation wind plant substation and the collector circuits showed that all the calculated protective ratios were above the adequate margins specified in the standard.
The results for the feeder circuit breaker switching transients, including current chopping, pre-striking, and restriking events, were all found to be effectively mitigated by even the smallest section of the wind plant collector cable capacitance. Therefore, an important conclusion from the simulation analysis was that no further mitigation measures for these events, such as snubber circuits, are required.
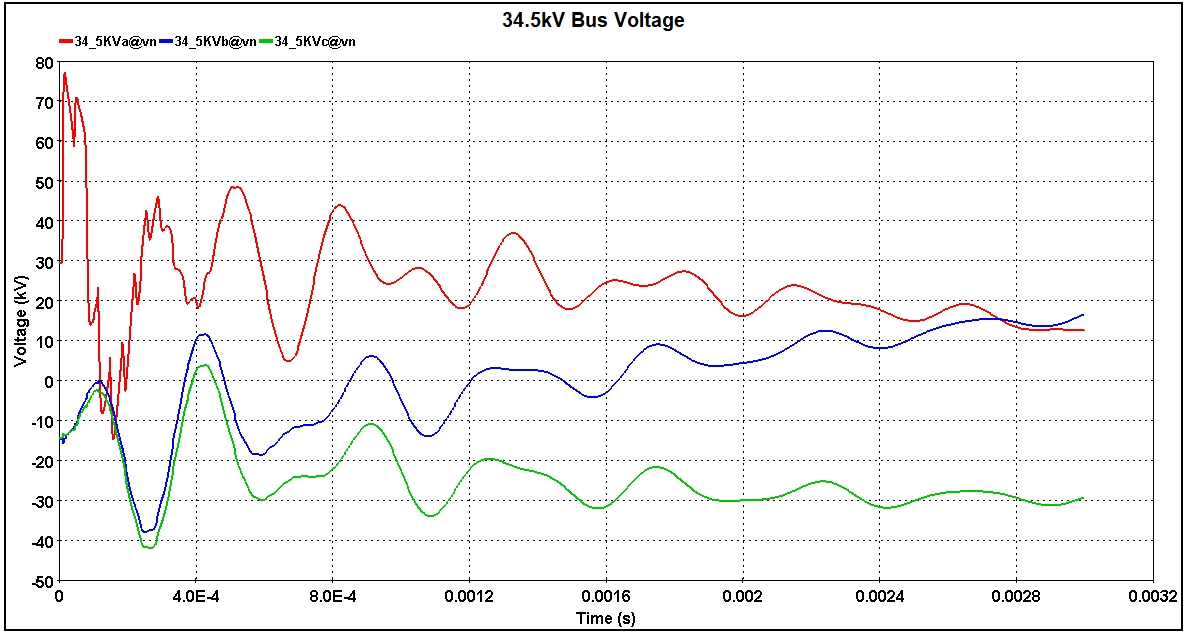
This study included a BIL rating lighting transient evaluation of the next generation wind plant equipment. The operating conditions involved having a lightning strike to the 34.5kV substation bus with the specification of the current waveform being 10kA magnitude, with an 8×20μsec characteristic. The operating conditions also included having the 34.5kV underground home-run cable section length of 10,030 feet. In addition, the 1,000-kVA grounding transformer and the riser pole surge arrester were both in-service during this analysis. The 34.5kV bus peak transient voltage (refer to Figure 1) was 77.205kV (2.74 per-unit). An important conclusion from the simulation analysis completed was that none of the proposed next generation wind plant equipment BIL ratings need to be changed based on the results.
This study included an NGR evaluation of the next generation wind plant substation. The results showed that the simulated single-phase NGR voltages for the 0.53Ω and 1.0Ω reactor cases were well below the respective 150/200 kV BIL ratings for the substation and feeder equipment.
EnerNex has extensive expertise performing power system studies investigating the high-frequency transients associated with wind plant collector circuit breaker opening-and-closing operations and lightning surge transients. These studies often require use of sophisticated digital simulation tools (e.g., EMTP-RV, PSCAD). Computer simulations provide a convenient means to characterize transient phenomena, determine resulting problems, and evaluate possible mitigation alternatives.
Figure 1 – 34.5kV Substation Bus Three-Phase Transient Voltage Waveforms during Lighting Strike